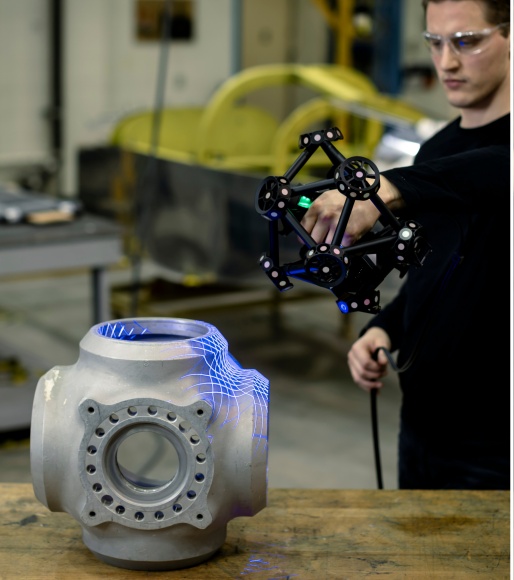

2026-01-29 Lasers are used in 3D scanning by projecting light onto an object and measuring the reflection to calculate distance, creating a detailed "point cloud" of millions of data points that form a 3D model. Scanners use methods like Time-of-Flight (ToF), measuring the time for pulses to return, or Laser Triangulation, using angles and known sensor positions to determine depth. This process captures precise geometric data for applications in architecture, engineering, gaming, and manufacturing.
Read More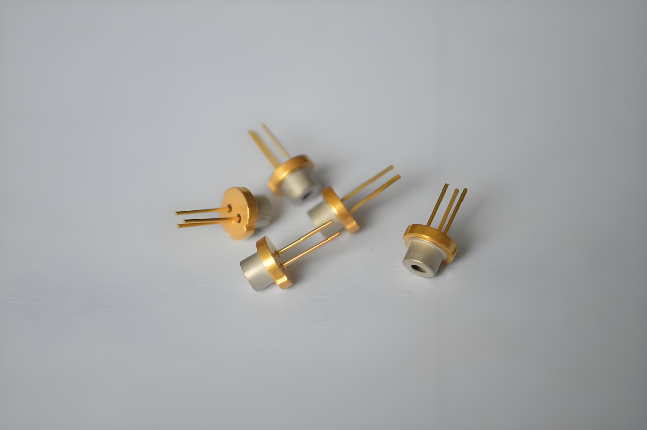 
2026-01-26 Light-emitting diodes (LED) and laser diodes (LD) both generate light via electron-hole recombination. They both have a PIN diode at their heart. Even their names sound similar.So, how are they different?Let’s start by looking at how each is used, before learning what design differences turn LEDs in
Read More 
2026-01-26 A laser diode is a semiconductor device that emits coherent light via stimulated emission, which is more complex and responsive than a light-emitting diode (LED). ‘Laser’ stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
Read More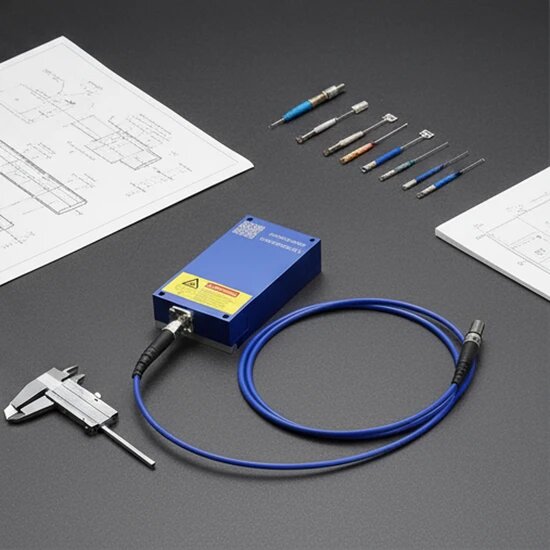 
2026-01-22 A Space Coupling Fiber Laser Module integrates laser diodes with optics (lenses, mirrors) to precisely focus and inject their light into an optical fiber, creating a compact, stable, high-quality beam delivery system, essential for applications needing precise light delivery, combining multiple diodes, or remote laser power in medical, industrial, or scientific fields.
Read More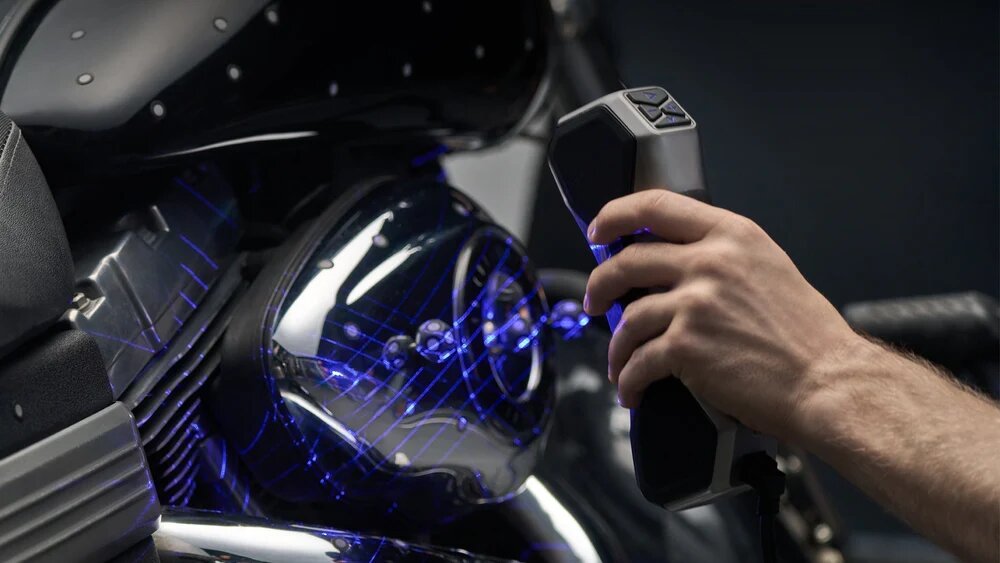 
2026-01-20 Simply put, laser 3D scanning is a process of capturing precise 3D information off any object or environment using a laser as a light source. The technology relies on laser beams to measure the distance to a surface and create ultra-realistic 3D models of objects, sites, and vast landscapes. 3D laser scanning is a popular engineering, construction, and architectural tool, commonly used to document and assess the condition of different structures.
Read More 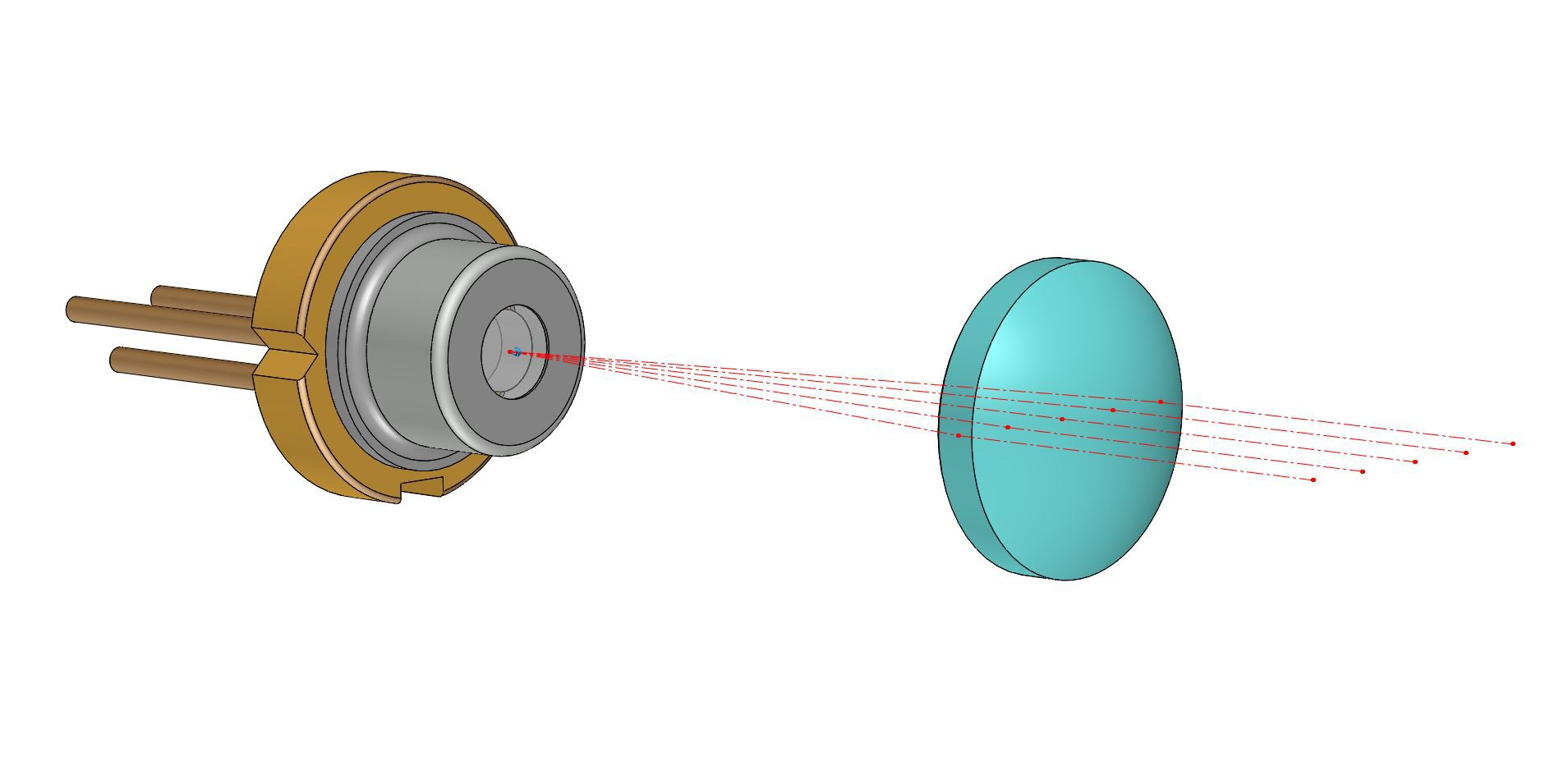
2026-01-17 If you want a smaller collimating laser beam, you must accept a larger divergence; On the contrary, if we want to keep the collimation of light over a long distance, it must have a larger beam size.
The laser beam is focused through the focal lens. The focal lens acts like a magnifying glass and sunlight. For a 55mm EFL lens, the laser beam passes through the lens and converges to the smallest point at about 55mm from the edge of the lens. The laser beam is concentrated to the smallest size at this "spot".
Read More 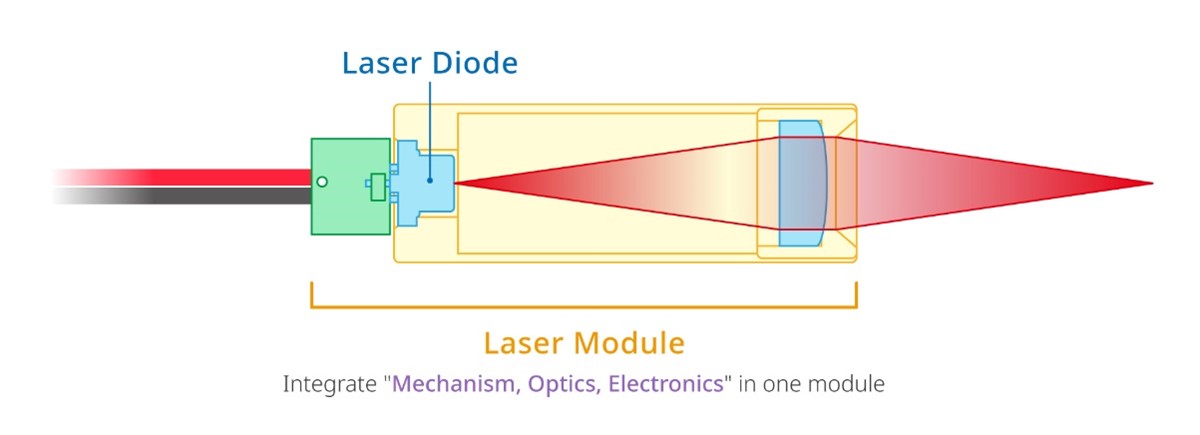
2026-01-13 Customizing a laser diode module requires careful planning and collaboration with experienced manufacturers to ensure the final product meets your exact application needs. Below is a comprehensive, actionable guide:
Read More 
2026-01-13 Fundamentally, a laser diode module incorporates a laser diode, one or more lenses, and drive electronics, packaged in a laser module housing. Laser modules are used in a wide range of applications from providing a visual guide for alignment applications to curing in 3D printing and enabling 3D measurement.
Read More 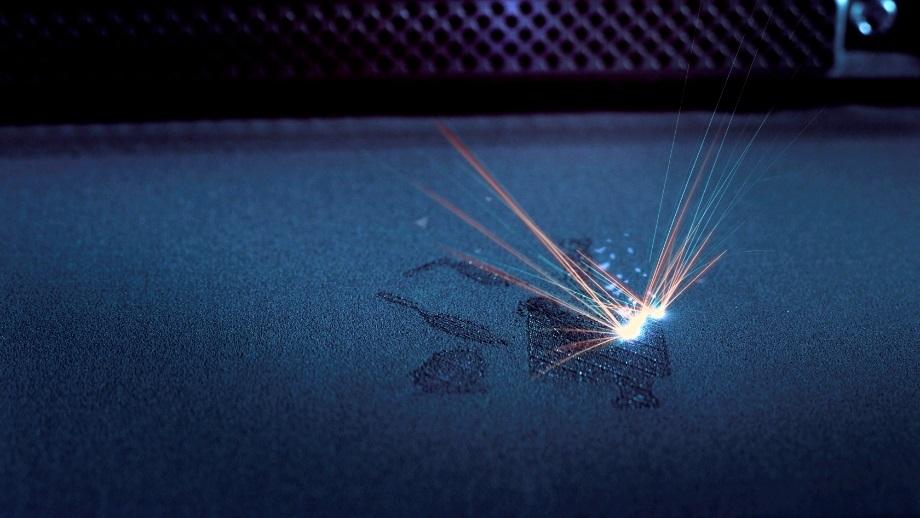
2026-01-10 In SLS (Selective Laser Sintering), blue diode lasers (around 445-450nm) are used as powerful, focused light sources to selectively melt and fuse fine polymer powder (like nylon) into solid 3D objects, layer by layer, by tracing cross-sections, with the laser's wavelength optimized for absorption by dark powders, allowing for strong, functional parts without supports.
Read More 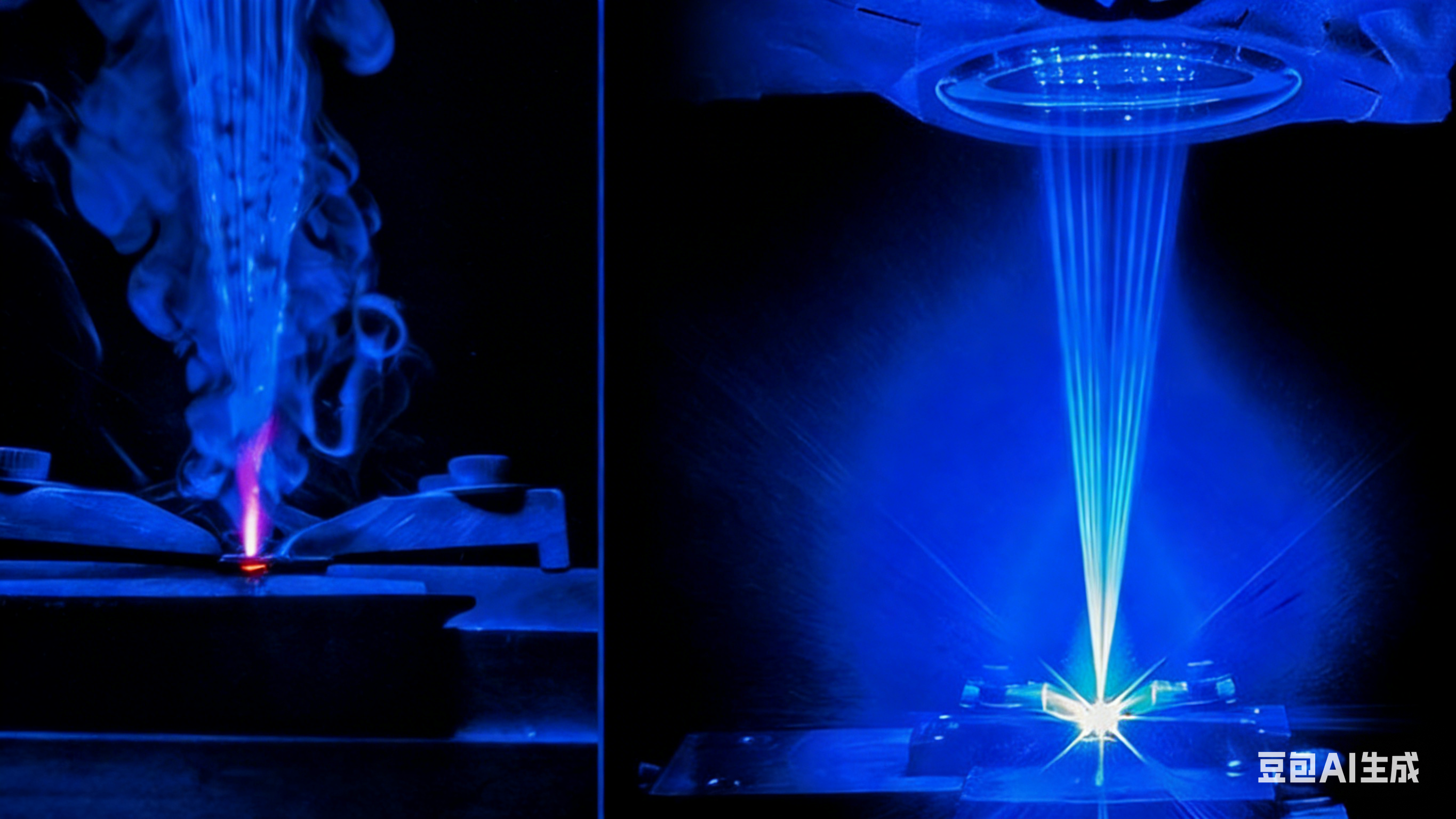
2026-01-10 Blue laser technology becomes the key to breakthrough! The challenge of highly reflective materials in 3D printing has been overcome, accelerating the arrival of the consumer market.
Read More 








